- On the Navigation pane, click Configuration > Network > Network to visit the Network page.
- Click New on the upper-left of the interface list.
- Select VLAN Interface from the drop-down list.
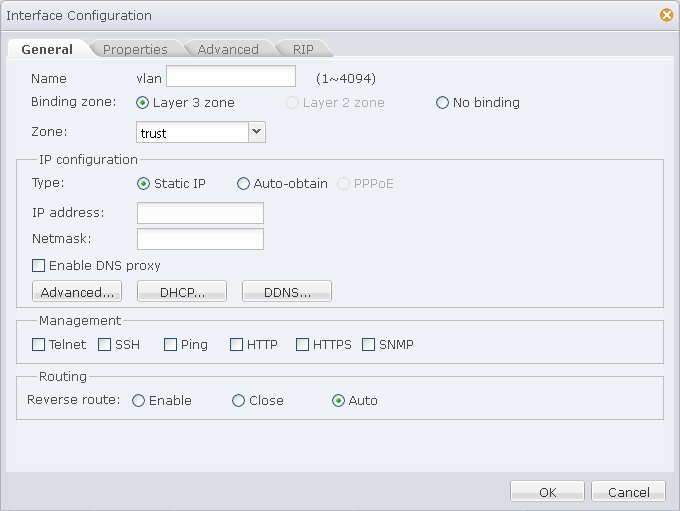
- In the Interface Configuration dialog shown above, specify a name. If necessary, type the description information into the Description text box.
- Specify the binding type. If Layer 3 zone is selected, also select a security zone from the Zone drop-down list.
- If Layer 3 zone is selected, in the IP Configuration section, configure IP related information for the interface. For detailed options, see the following instructions:
Type Description Static IP IP address: Specifies an IP address for the interface. Netmask: Specifies a netmask for the interface. Enable DNS Proxy: Select this checkbox to enable DNS proxy for the interface. Advanced Management IP: Specifies a management IP for the interface. Type the IP address into the box. Secondary IP: Specifies secondary IPs for the interface. You can specify up to 6 secondary IP addresses. DHCP: In the DHCP Configuration dialog, configure DHCP related options for the interface. For detailed instructions, see Configuring DHCP. DDNS: In the DDNS Configuration dialog, configure DDNS related options for the interface. For detailed instructions, see Configuring a DDNS. Auto-obtain Set gateway information from DHCP server as the default gateway route: With this checkbox selected, StoneOS will set the gateway information provided by the DHCP server as the default gateway route. Advanced Distance: Specifies a route distance. The value range is 1 to 255. The default value is 1. Weight: Specifies a route weight. The value range is 1 to 255. The default value is 1. Management Priority: Specifies a priority for the DNS server. Except for static DNS servers, StoneOS can also learn DNS servers dynamically via DHCP or PPPoE. Therefore, you need to configure priorities for the DNS servers, so that the system can choose a DNS server according to its priority during DNS resolution. The priority is represented in numbers from 1 to 255. The larger the number is, the higher the priority is. The priority of static DNS servers is 20. DDNS: In the DDNS Configuration dialog, configure DDNS related options for the interface. For detailed instructions, see Configuring a DDNS. - If Layer 3 zone is selected, in the Management section, select one or more management method checkboxes.
- In the Routing section, enable or close reverse route as needed. The options are:
Enable: Enforces to use a reverse route. If the reverse route is not available, packets will be dropped. This option is enabled by default.
Close: Reverse route will not be used. When reaching the interface the reverse data stream will be returned to its original route without any reverse route check. That is, reverse packets will be sent from the ingress interface that initializes the packets.
Auto: Reverse route will be prioritized. If available, the reverse route will be used to send packets; otherwise the ingress interface that initializes the packets will be used as the egress interface that sends reverse packets. - If needed, click the Properties tab to configure properties for the interface. For detailed options, see the following instructions:
MTU: Specifies a MTU for the interface. The value range is 1280 to 1500/1800 bytes. The default value is 1500. The max MTU may vary from different Hillstone models.
ARP learning: Select the Enable checkbox to enable ARP learning.
ARP Timeout: Specifies an ARP timeout for the interface. The value range is 5 to 65535 seconds. The default value is 1200.
Keep-alive IP: Specifies an IP address that receives the interface's keep-alive packets.
MAC clone: Changes the MAC address of the interface. - If needed, click the Advanced tab to configure advanced options for the interface, including Shutdown and Monitor and Backup options. For detailed options, see the following instructions:
Function Configuration Shutdown StoneOS supports interface shutdown. You can not only enforce to shut down a specific interface, but also control the time of shutdown by schedule, or control the shutdown according to the link status of tracked objects. Configure the options as below:
- Select the Shut down checkbox to enable interface shutdown.
- To control the shutdown by schedule or tracked objects, select an appropriate checkbox, and then select an appropriate schedule or tracked object from the drop-down list.
Monitor and Backup Configure the options as below:
- Select an appropriate checkbox, and then select an appropriate schedule or tracked object from the drop-down list.
- Select an action: Shut down the interface: During the time specified in the schedule, or when the tracked object fails, the interface will be shut down and its related route will fail; Migrate traffic to backup interface: During the time specified in the schedule, or when the tracked object fails, traffic to the interface will be migrated to the backup interface. In such a case you need to select a backup interface from the Backup interface drop-down list and type the time into the Migrating time box. (Migrating time, 0 to 60 minutes, is the period during which traffic is migrated to the backup interface before the primary interface is switched to the backup interface. During the migrating time, traffic is migrated from the primary interface to the backup interface smoothly. By default the migrating time is set to 0, i.e., all the traffic will be migrated to the backup interface immediately.)
- If needed, click the RIP tab to configure RIP for the interface. For detailed options, see the following instructions:
Authentication mode: Specifies a packet authentication mode for the system, including plain text (the default) and MD5. The plain text authentication, during which unencrypted string is transmitted together with the RIP packet, cannot assure security, so it cannot be applied to the scenarios that require high security.
Authentication string: Specifies a RIP authentication string for the interface.
Transmit version: Specifies a RIP information version number transmitted by the interface. By default V2 RIP information will be transmitted.
Receive version: Specifies a RIP information version number received by the interface. By default V2 RIP information will be received.
Split horizon: Select the Enable checkbox to enable split horizon. With this function enabled, routes learned from an interface will not be sent from the same interface, in order to avoid routing loop and assure correct broadcasting to some extent. - Click OK to save your settings.
 to add to the Selected VLANs list.
to add to the Selected VLANs list.